

نوع مقاله : گزارش مورد
نویسندگان
1 مرکز تحقیقات دستگاه گوارش، واحد توسعه تحقیقات بالینی بیمارستان اما م خمینی، دانشکده پزشکی، دانشگاه علوم پزشکی جندی شاپور اهواز، اهواز، ایران
2 مرکز تحقیقات دستگاه گوارش، واحد توسعه تحقیقات بالینی بیمارستان امام خمینی، دانشکده پزشکی، دانشگاه علوم پزشکی جندی شاپور اهواز، اهواز، ایران
چکیده
کلیدواژهها
موضوعات
Introduction
In the past decades, the treatment of Zenker's diverticulum in the esophagus was performed by surgical resection [1]. The invention of endoscopic methods and tools and minimally invasive surgeries have changed this method of treatment; today, the Zenker's diverticulum can be treated easily with minimal risk using a flexible endoscope [2, 3].
Case Report
The patient was a 95-year-old woman who presented with chronic cough, inability to swallow liquids and solids, loss of appetite, and weight loss for 6 months. At first, the primary diagnosis was food stuck in the esophagus; after several unsuccessful endoscopy, a closed end was observed at the beginning of the esophagus, which suggested to be the Zenker's diverticulum. A barium swallow radiography was requested for the patient, but she was not able to do due to severe disability. Therefore, the food residue was removed by the basket and the large Zenker's diverticulum was observed next to the entrance of the esophagus. After determining the cause of dysphagia due to a large Zenker's diverticulum, and the inability of patient to tolerate surgery due to her age and general deterioration, she underwent the endoscopic diverticulectomy which was the first case in southwestern Iran. Under a two-hour endoscopic surgery, the wall of the cricopharyngeal muscle was first identified. After passing the guidewire, an NG tube was inserted to keep the esophagus open, and diverticulectomy was then performed by cutting the muscle with an endoscopic needle knife, using the Olympus flexible endoscope and closing the surgery site with clips. There were no complications during or after the surgery. The patient was kept fasting for 48 hours. After that, liquid feeding was started; 5 days later, the patient was discharged from the hospital with a good general condition and the ability to swallow food.
Discussion
Zenker's diverticulum is an uncommon condition that usually manifests itself in the seventh or eighth decade of life and is diagnosed by endoscopy or barium swallow test [4, 5]. In the last decade, the effectiveness of endoscopic methods for the treatment of Zenker's diverticulum has been proven as an effective and less complicated treatment compared to surgery. Endoscopic methods include the use of a rigid or flexible endoscope to cut the diverticulum septum. The rigid approach through the mouth requires placing a rigid diverticuloscope and cutting the cricopharyngeal muscle with a knife. The main limitations of this method include the need for general anesthesia and relative contraindications in those with limited movements of the cervical vertebrae. For this reason, the technique of using a flexible endoscope is preferred for this procedure [6]. This method requires a high resolution flexible endoscope, electrosurgical knife, coagulation forceps, guidewire and nasogastric tube. Using a diverticuloscope to keep the septum stable is optional and depends on the skill and experience of the surgeon. Cutting the cricopharyngeal muscle is done with a knife; various types of knives are used for this purpose including hook knife, scissor-like knife, and triangular knife. Among these, the most used ones are needle knife and hook knife [7]. The procedure can be performed while the patient is asleep with propofol, and its steps include cleaning the diverticulum of food residues and then placing a nasogastric tube in the esophagus to keep its channel open. Then the septum is cut with a knife. After cutting the muscle fibers at the bottom of the wall, its sides are closed with clips to prevent possible bleeding or perforation [8]. The success rate of this method is about 80-90% and possible rare complications include bleeding and perforation [5].
The case reported in this study was the first case of endoscopic diverticulectomy in the southwest of Iran, during which the patient regained her health and was discharged from the hospital after 5 days with a good general condition and the ability to swallow liquids and solids.
Endoscopic diverticulectomy is a safe method for treating Zenker's diverticulum, especially in cases where the deterioration of the patient's condition make surgical methods risky.
Ethical Considerations
Compliance with ethical guidelines
This study is a case study and does not require a code of ethics.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Authors' contributions
All authors contributed equally in preparing all parts of the research.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declared no conflict of interest
Acknowledgements
We thank Mr. Abbas Hashempour as an assistant in performing the endoscopic procedure.
مقدمه
در گذشته درمان دایورتیکول زنکر مری به وسیله رزکسیون جراحی انجام میشد [1]. در حالی که ابداع روشها و ابزار آندوسکوپیک و جراحیهای کم تهاجمی این روش درمان را تغییر داده است. امروزه دایورتیکول زنکر مری به آسانی و با کمترین خطر با آندوسکوپ انعطافپذیر قابل درمان است [2، 3].
گزارش بیمار
بیمار، خانم 95 سالهای است که با سرفه مزمن، عدم توانایی بلع مایعات و جامدات، کاهش اشتها و کاهش وزن از شش ماه قبل مراجعه کرده بود که در ابتدا تشخیص اولیه گیر کردن مواد غذایی در مری بود، اما پس از چند بار آندوسکوپی ناموفق، یک انتهای بسته در ابتدای مری ملاحظه شد که مطرحکننده دایورتیکول زنکر در ابتدای مری بود.
برای بیمار گرافی با بلع باریوم درخواست شد که بهدلیل ناتوانی شدید، قادر به انجام آن نبود. بنابراین باقیمانده غذا توسط بسکت خارج و مجرای بزرگ دایورتیکول در کنار ورودی مری ملاحظه شد (تصویر شماره 1).
پس از مشخص شدن دلیل دیس فاژی، بهدلیل دایورتیکول بزرگ زنکر در قسمت ابتدایی مری و عدم توانایی تحمل جراحی بهدلیل شرایط سنی و وخامت حال عمومی، یک دایورتیکولکتومی آندوسکوپیک برای بیمار برنامهریزی شد و بیمار تحت اولین دایورتیکولکتومی آندوسکوپیک در جنوب غرب ایران قرار گرفت و با یک عمل دو ساعته آندوسکوپیک، ابتدا دیواره عضله کریکوفارنژیوس شناسایی شد و پس از عبور دادن گاید وایر، یک لوله NG برای باز نگه داشتن مجرای مری تعبیه شد (تصاویر شماره 2 و 3) و دایورتیکولکتومی از طریق برش عضله با نیدل نایف آندوسکیپی با استفاده از آندوسک انعطافپذیر الیمپوس و بستن محل عمل با کلیپس انجام شد (تصاویر شماره 4، 5 و 6).
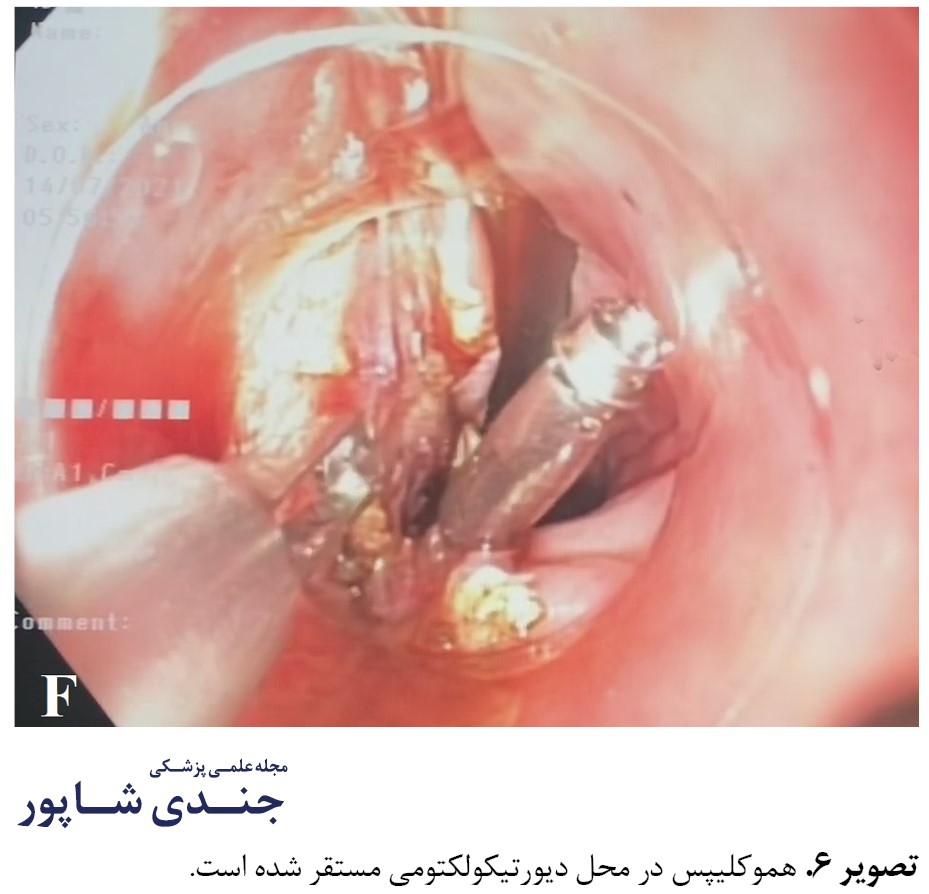
هنگام و پس از عمل، هیچگونه عارضهای ایجاد نشد. سپس بیمار به مدت 48 ساعت ناشتا نگه داشته شد. سپس ابتدا تغذیه با مایعات شروع شد و پنج روز بعد بیمار با حال عمومی خوب و توانایی بلع غذا از بیمارستان مرخص شد. این عمل آندوسکوپیک اولین مورد انجامشده در جنوب غرب ایران است.
بحث
دایورتیکول زنکر یک وضعیت غیرمعمول است که معمولاً در دهه هفتم و یا هشتم زندگی تظاهر یافته است و توسط آندوسکوپی و یا گرافی با بلع باریوم تشخیص داده میشود [4، 5]. در دهه اخیر، کارایی روشهای آندوسکوپیک برای درمان دایورتیکول زنکر بهعنوان یک درمان مؤثر و کم عارضه در مقایسه با جراحی اثبات شده است. روشهای آندوسکوپیک شامل استفاده از آندوسکوپ ریجید یا انعطافپذیر برای بریدن سپتوم دایورتیکول است. رویکرد ریجید از طریق دهان، نیازمند قرار دادن یک دایورتیکولوسکوپ ریجید و بریدن عضله کریکوفارنژیوس به وسیله نایف است.
محدودیتهای اصلی این روش شامل نیاز به بیهوشی جنرال و کنترااندیکاسیون نسبی در کسانی که دچار محدودیت در حرکات مهره های گردنی هستند. به همین دلیل عمدتاً تکنیک استفاده از آندوسکوپ انعطافپذیر برای این پراسیجر ترجیح داده میشود [6].
این روش نیازمند یک آندوسکوپ انعطافپذیر با رزولوشن بالا، نایف الکتروسارجیکال، فورسپسهای کواگولاسیون، گایدوایر و لوله نازوگاستریک است. استفاده از دایورتیکولوسکوپ برای ثابت نگه داشتن سپتوم اختیاری است و بستگی به مهارت و تجربه فرد اپراتور دارد. بریدن عضله کریکوفارنژیوس توسط نایف انجام شد که در این زمینه انواع نایفها شامل نایف هوک، نایف شبیه قیچی (سیزر) و نایف سهگوش کاربرد دارند و از این میان پرکاربردترینها نیدل نایف و نایف هوک هستند [7].
پراسیجر را میتوان در شرایطی که بیمار با پروپوفول بهخوابرفته انجام داد و مراحل آن شامل پاکسازی دایورتیکول از باقیماندههای غذایی و سپس قرار دادن لوله نازوگاستریک در مری برای باز نگه داشتن مجرای آن است. سپس سپتوم به وسیله نایف بریده شده و پس از قطع رشتههای عضلانی در کف دیواره، طرفین آن با کلیپس برای پیشگیری از خونریزی یا پرفوراسیون احتمالی بسته میشود [8].
موفقیت این روش حدود 80 تا 90 درصد بود و عوارض احتمالی نادر شامل خونریزی و پرفوراسیون است [5]. مورد گزارششده در این مقاله، اولین مورد دایورتیکولکتومی آندوسکوپیک در جنوب غرب ایران است که طی آن، بیماری که بهدلیل سن بالا و شرایط عمومی، قابل عمل کردن نبود، سلامت خود را باز یافته و پس از پنج روز با حال عمومی خوب و توانایی بلع مایعات و جامدات از بیمارستان مرخص شد.
نتیجهگیری
دایورتیکولکتومی آندوسکوپیک یک روش مطمئن و بیخطر برای درمان دایورتیکول زنکر است، بهویژه در مواردی که شرایط و وخامت حال بیمار، انجام عمل جراحی را پرخطر میکند.
ملاحظات اخلاقی
پیروی از اصول اخلاق پژوهش
این مطالعه، یک مقاله موردی است و به کد اخلاق نیاز ندارد.
حامی مالی
این پژوهش هیچگونه کمک مالی از سازمانیهای دولتی، خصوصی و غیرانتفاعی دریافت نکرده است.
مشارکت نویسندگان
تمام نویسندگان در آمادهسازی این مقاله مشارکت داشتند.
تعارض منافع
بنابر اظهار نویسندگان، این مقاله تعارض منافع ندارد.
تشکر و قدردانی
از آقای عباس هاشمپور بهعنوان دستیار انجام پراسیجر آندوسکوپیک تشکر میشود.
References
References